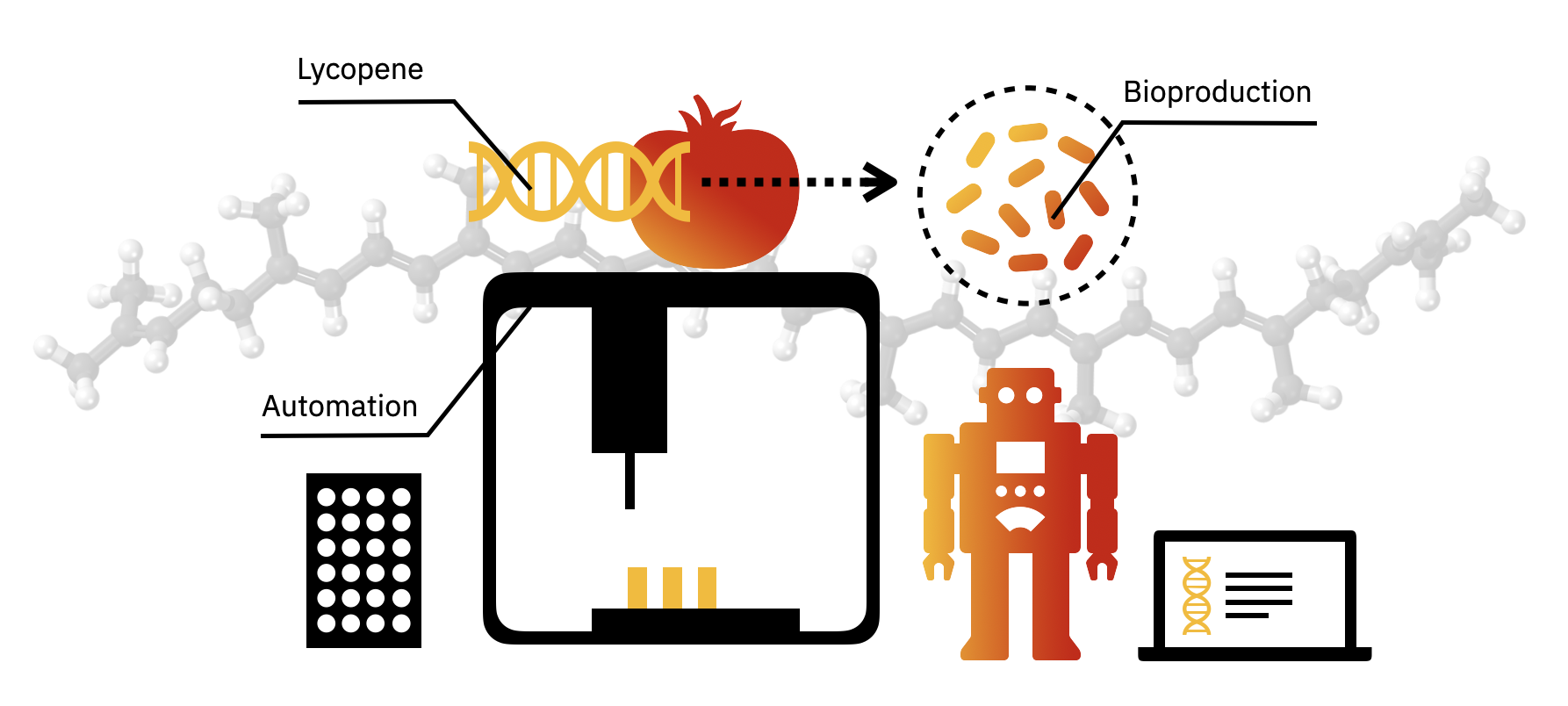

Lycopene is the red pigment that gives tomatoes their color. This pigment is also made by microbes. In fact, transferring a 3-enzyme pathway to E. coli can convert farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) to lycopene. The computational tools and databases presented today can also be used to enhance lycopene production in E. coli or even produce different colors, such as the beta-carotene pigment that makes carrots orange.
For the laboratory portion of this assignment, you will characterize lycopene production in the E. coli strain from Addgene with the pAC-LYC plasmid. You will also characterize beta-carotene production in E. coli from Addgene with the pAC-BETA plasmid. Note, the pAC-LYC plasmid contains three genes from Erwinia herbicola: CrtE, CrtI, and CrtB. The pAC-BETA plasmid produces beta-carotene through the addition of the Erwinia herbicola crtY gene. All plasmids include the gene for chloramphenicol resistance.
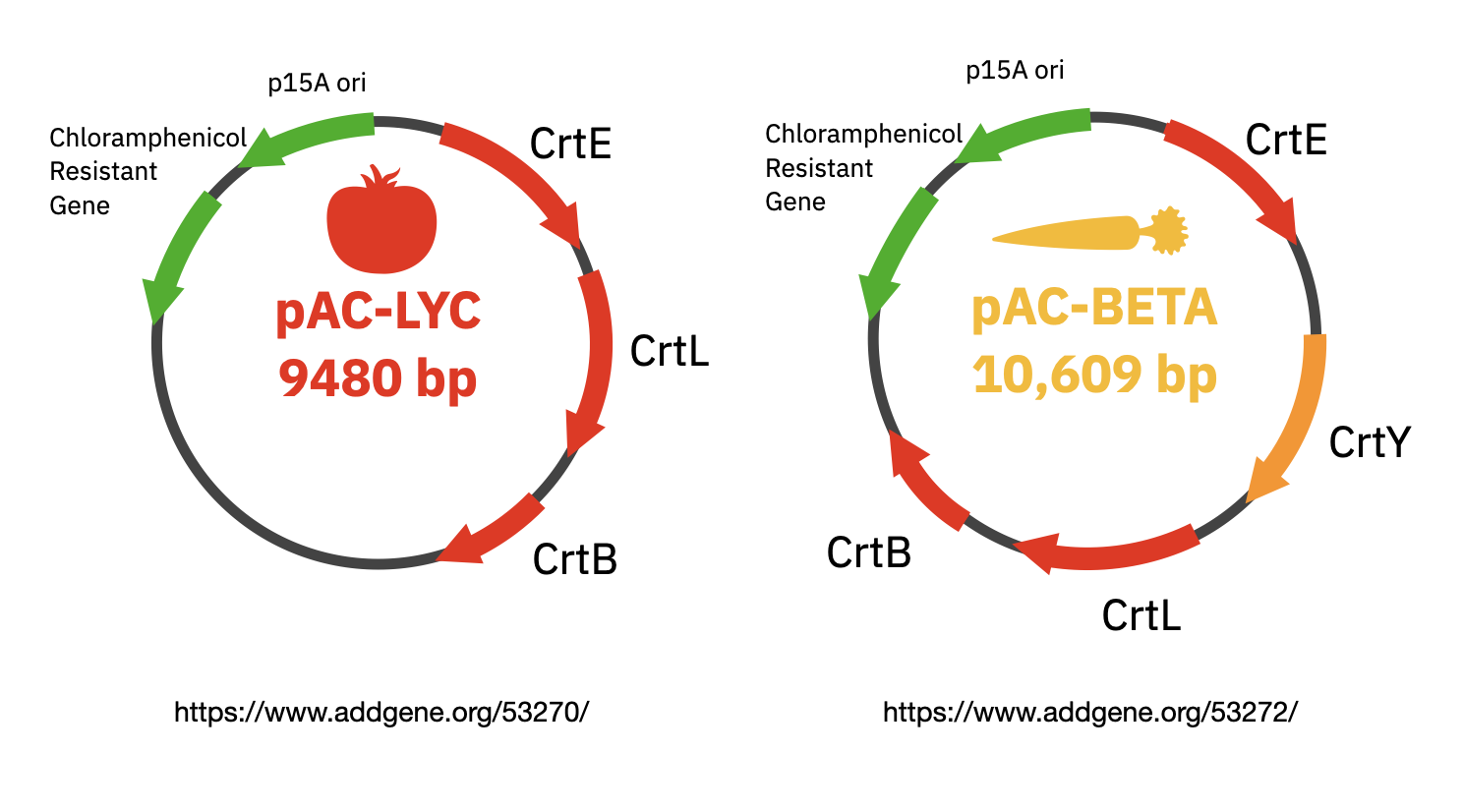
Plasmids involved in the experiment.
Part A: Open-Ended Questions
Part B: Plasmids 101
Part C: Labwork - Bioproduction: Plasmids, Growth, Measurement
Pick a plasmid from this list of highly requested plasmids and identify:
Describe in a sentence what this plasmid would be used for.